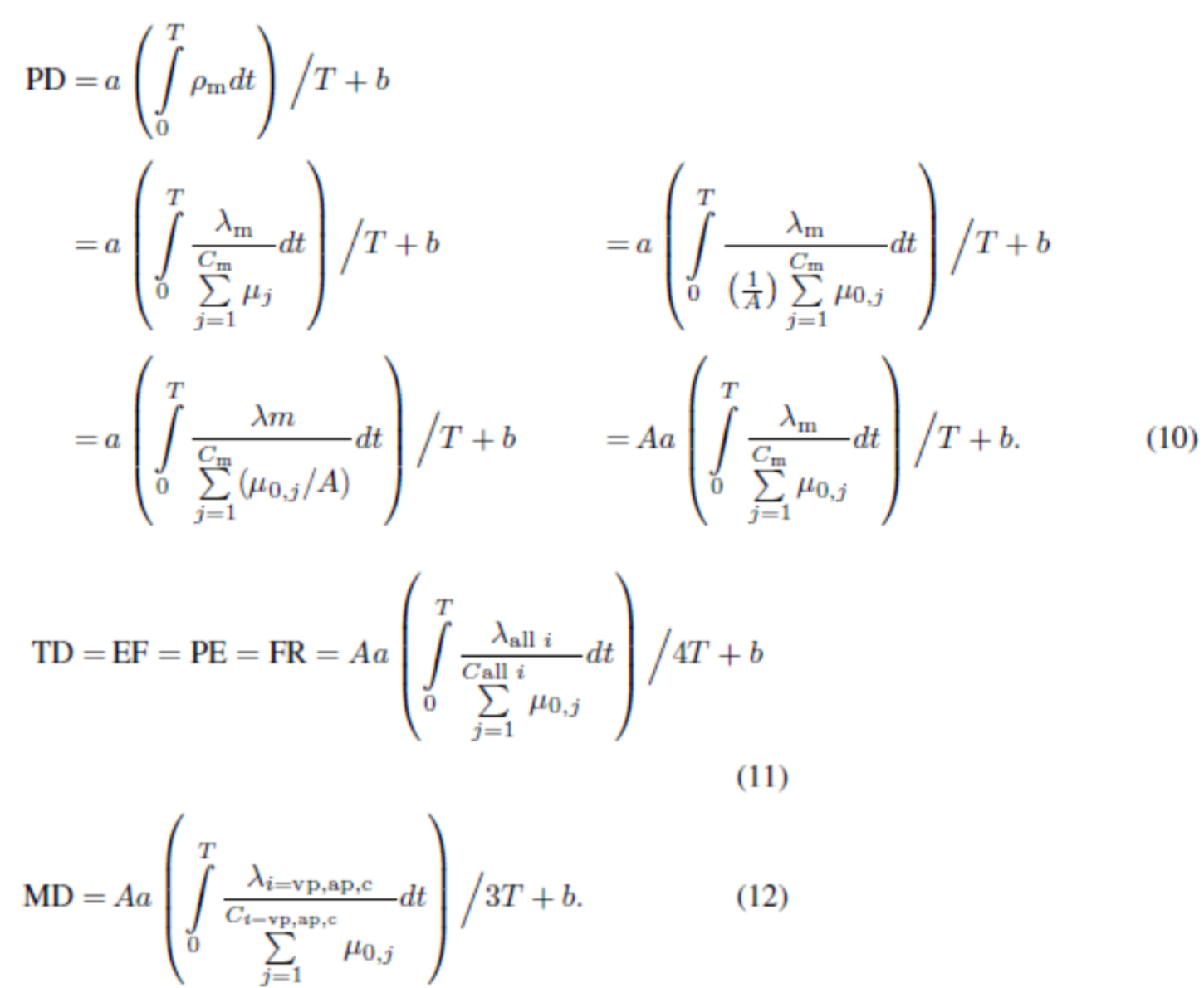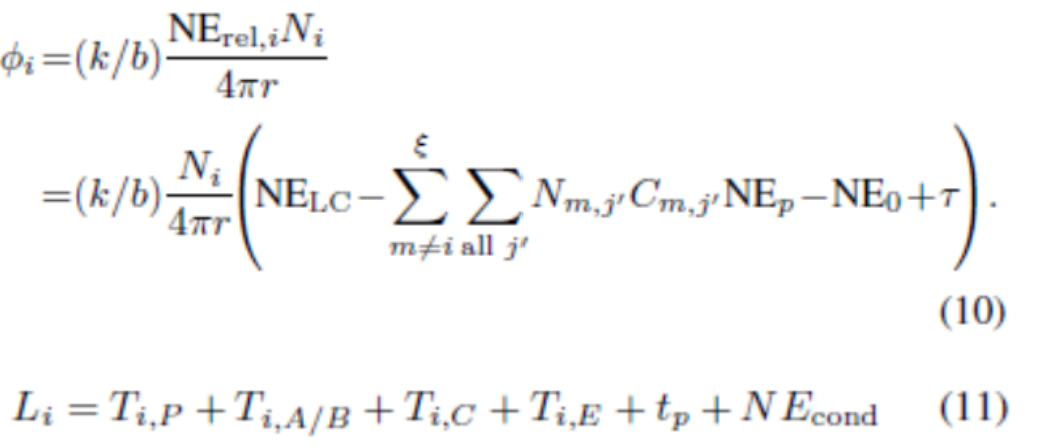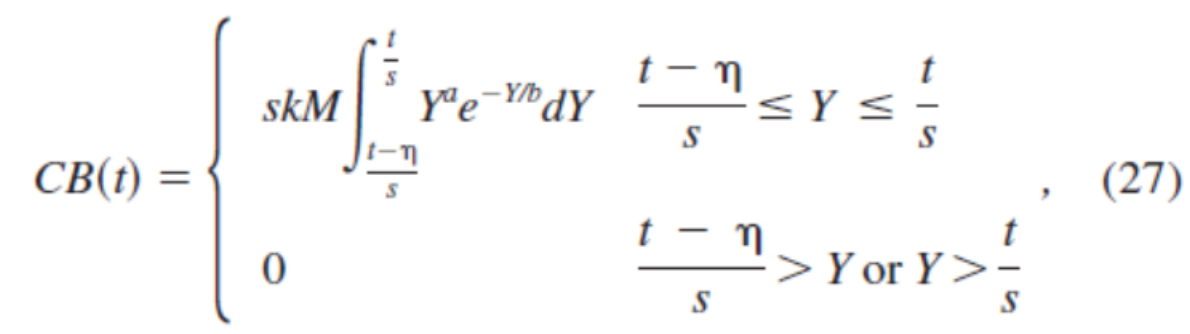1.建模报告
1.1 人的建模系列报告1:基于QN-MHP模型的SPO人机功能分配研究

报告人:中国民航大学 邵铿睿
报告时间:2023年1月14日下午2点
腾讯会议号:712-585-898
报告摘要:为探究未来单一飞行员驾驶模式下的驾驶舱人机交互及功能分配方法,选取单发失效场景利用QN-MHP模型对飞行员的工作负荷进行建模仿真并进行实验验证,结果表明:QN-MHP模型适用于飞行员的工作负荷建模;优化后的SPO人机功能分配能够提高视觉搜索效率,降低工作负荷及个体疲劳程度。
版权声明:本视频版权属于人因百科网站所有,如需要视频请联系我们,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意(
renyinbaike@163.com)。
鸣谢:心行者科技(杭州)有限责任公司对本系列讲座的支持。本研究使用的是该公司出品的人的认知和行为仿真软件:人的认知和行为仿真软件(企业基础版)(
http://www.shuziwo.com/product.html)。
本视频百度网盘链接:基于QN-MHP模型的SPO人机功能分配研究.mp4,提取码: 9zvm
1.2 人的建模系列报告2:汽车智能座舱人机交互建模研究

报告人:清华大学 李欣璘
报告时间:2023年3月18日下午2点
腾讯会议号:167-507-964
报告摘要:驾驶智能座舱的设计多种多样,选取驾驶人地址输入任务,使用人的信息加工排队网络模型 (QN-MHP)对驾驶人与智能座舱的语音交互以及触控屏交互进行计算建模。行为实验结果表明,使用人的认知和行为仿真软件,该模型能够根据不同的智能座舱设计参数,比较准确地预测驾驶人的驾驶任务行为、驾驶安全情况、和第二任务智能座舱操作绩效,协助智能座舱设计人员更快更好地设计智能座舱。
版权声明:本视频版权属于人因百科网站所有,如需要视频请联系我们,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意(
renyinbaike@163.com)。
鸣谢:心行者科技(杭州)有限责任公司对本系列讲座的支持。本研究使用的是该公司出品的人的认知和行为仿真软件:人的认知和行为仿真软件(企业基础版)(
http://www.shuziwo.com/product.html)。

1.3 人的建模和仿真系列报告3:有人/无人机协同作战战机智能座舱人机交互建模研究

报告人:石河子大学 魏子凯
报告时间:2023年5月27日下午2点
腾讯会议号:456-337-891
报告摘要:为了研究有人/无人协同作战场景多任务条件下飞行员工作绩效,设计了不同智能座舱显示界面,使用人的信息加工排队网络模型 (QN-MHP)对飞行员与智能座舱AI系统交互进行建模,对比不同显示界面设计方案对飞行员第二任务操作绩效的影响,同时对不同G过载情况下飞行员的驾驶绩效进行建模,结果表明:基于QN-MHP模型的预测,第二种设计方案,更适用于战机飞行员多任务和G过载场景,并能够大量节省实验时间和风险。
版权声明:本视频版权属于人因百科网站所有,如需要视频请联系我们,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意(
renyinbaike@163.com)。
鸣谢:心行者科技(杭州)有限责任公司对本系列讲座的支持。本研究使用的是该公司出品的人的认知和行为仿真软件:人的认知和行为仿真软件(企业基础版)(
http://www.shuziwo.com/product.html)。
1.4 人的建模和仿真系列报告4:认知建模服务核电人机界面设计

报告人:浙江大学 潘嘉蔚
报告时间:2023年10月7日下午2点
腾讯会议号:215-786-272
报告摘要:核电厂主控室操作系统往往界面复杂、设计多样,如何改进核电操作人机界面设计以降低人误概率、保障系统安全有着重要的研究意义。使用嵌入QN-MHP-U的人的认知和行为仿真软件(企业版),对核电厂操作员进行核电事故处理的操控任务进行仿真建模。仿真实验结果表明,模型能够根据界面设计参数和任务流程,预测核电厂操作员的操作时间和工作负荷等,节省90%以上的行为实验时间和经费,从而协助核电厂主控室人机界面设计人员更低成本且高效率地改进核电人机操作系统的界面布局和交互方式。
版权声明:本视频版权属于人因百科网站所有,如需要视频请联系我们,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意(
renyinbaike@163.com)。
鸣谢:心行者科技(杭州)有限责任公司对本系列讲座的支持。本研究使用的是该公司出品的人的认知和行为仿真软件:人的认知和行为仿真软件(企业基础版)(
http://www.shuziwo.com/product.html)。
本视频百度网盘链接:认知建模服务核电人机界面设计.mp4,提取码: byc3
1.5 人的建模和仿真系列报告5:认知建模服务智能语音系统设计
报告人:清华大学 章薇
报告时间:2023年10月15日(周日)下午2点
腾讯会议号:421-189-042
报告摘要:随着语音识别和自然语言处理技术的发展,具有识别和对话功能的智能语音助手正广泛应用于现实场景中。语音交互系统具有不同的设计和性能参数,如何设计和评估语音交互系统以提升人机语音交互绩效和用户体验具有重要的研究意义。使用嵌入QN-MHP-U的人的认知和行为仿真软件,对人机语音交互任务进行仿真建模,报告侧重讲解实体在模型中的路径的设置。仿真实验结果表明,该模型能根据系统参数和任务流程,预测人机语音交互任务的完成时间、用户的工作负荷和用户满意度,模型的预测得到了人机语音交互实验的验证。仿真建模节省实验95%以上的时间和经费,从而能协助语音交互系统设计开发人员更低成本且高效率地评估和优化人机语音交互系统的参数设计。
版权声明:本视频版权属于人因百科网站所有,如需要视频请联系我们,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意(
renyinbaike@163.com)。
鸣谢:心行者科技(杭州)有限责任公司对本系列讲座的支持。本研究使用的是该公司出品的人的认知和行为仿真软件:人的认知和行为仿真软件(企业基础版)(
http://www.shuziwo.com/product.html)。
本视频百度网盘链接:认知建模服务智能语音系统设计.mp4,提取码: qd5h
1.6 人的建模和仿真系列报告6:认知建模服务工业机器人界面设计

报告人:清华大学 游仙文
报告时间:2024年1月20日(周六)下午2点
腾讯会议号:168-973-851
报告摘要:随着工业智能化和自动化的发展,工业机器人在工业任务中的运用越来越普遍。由于工业生产的复杂性以及时效性,设计一个合适的工业机器人交互界面来帮助操作人员更加高效、可靠地完成生产任务便成为了一个亟待解决的问题。本研究使用QN-MHP-U的人的认知和行为仿真软件(企业版),对工业机器人交互界面设计如何影响任务绩效和工作负荷进行了仿真建模。仿真结果显示了不同交互界面下的任务绩效和工作负荷差异,同时实验结果验证了QN-MHP-U模型的预测。
版权声明:本视频版权属于人因百科网站所有,如需要视频请联系我们,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意(
renyinbaike@163.com)。
鸣谢:心行者科技(杭州)有限责任公司对本系列讲座的支持。本研究使用的是该公司出品的人的认知和行为仿真软件:人的认知和行为仿真软件(企业基础版)(
http://www.shuziwo.com/product.html)。
1.7 人的建模和仿真系列报告7:基于排队网络模型的汽车控件设计快速评估方法

报告人:北京理工大学 设计与艺术学院 左孝林
报告时间:2024/06/09 10:00-11:00 北京时间
腾讯会议号:848-471-863
报告摘要:本文通过QN-MHP-U 模型来评估汽车驾驶系统的人体工程学性能,旨在比汽车领域传统的实验性人因研究更具时间和成本效益地改进汽车控件设计。研究方法 对三种典型乘用车的不同驾驶员交互控件(如危险灯开关、方向盘按钮)的空间坐标和尺寸等参数进行了实车测量,并将其整合到 QN-MHP-U 模型中,用于模拟驾驶员操作行为和预测任务表现来评估汽车控制设计的人体工程学得分。最后得出结论:嵌入QN-MHP-U 模型的人的认知和行为仿真软件,为评估和比较汽车驾驶系统中的车辆控件设计提供了一个系统的、普遍适用的解决方案。这使得汽车设计师能够从人体工程学的角度,更有效地评估和改进汽车控制设计,从而节约时间和经济成本。本工作已被国际人因工程和工效学会(Human Factors and Ergonomics Society)接收,并将于今年秋季在美国凤凰城国际HFES大会上进行大会报告。
版权声明:本视频版权属于人因百科网站所有,如需要视频请联系我们,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意(
renyinbaike@163.com)。
鸣谢:心行者科技(杭州)有限责任公司对本系列讲座的支持。本研究使用的是该公司出品的人的认知和行为仿真软件:人的认知和行为仿真软件(企业基础版)(
http://www.shuziwo.com/product.html)。
1.8 人的建模和仿真系列报告8:舰载机着舰任务认知行为仿真建模研究

报告人:河南工业大学 机电工程学院 顾森
报告时间:2024年9月22日上午10点
腾讯会议号:284-971-215
报告摘要:由于舰载机任务及使用场景的复杂性,对其人机操控界面优化设计方案的评价与验证较为困难。本研究以舰载机着舰任务为牵引,使用QN-MHP模型来预测不同人机操控界面设计方案下的飞行员操作绩效,旨在高效、快速的对舰载机人机操控界面设计方案进行评估。通过整理公开资料,研究了公开的舰载机人机操控界面中的控件尺寸位置与舰载机着陆任务操作规范,并将其整合到嵌入QN-MHP-U 模型的人的认知和行为仿真软件,用于模拟飞行员认知与操作行为,实现对任务绩效的预测。仿真结果显示了不同人机操控界面下的任务绩效和工作负荷差异,为评估和比较舰载机人机操控界面设计提供了一个系统且高效的解决方案。
版权声明:本视频版权属于人因百科网站所有,如需要视频请联系我们,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意(
renyinbaike@163.com)。
鸣谢:心行者科技(杭州)有限责任公司对本系列讲座的支持。本研究使用的是该公司出品的人的认知和行为仿真软件:人的认知和行为仿真软件(企业基础版)(
http://www.shuziwo.com/product.html)。
1.9人的建模和仿真系列报告9:多任务(Multitasking)情况下人的认知负荷建模和预测研究

在执行复杂多任务(Multitasking)过程中,操作员因需同时处理多项任务而往往可能引发认知负荷过载等问题。 本次在线报告分享对操作员在多任务场景(MATB多任务场景)中的认知过程进行精细化计算建模。借助嵌入QN-MHP-U模型的人的认知和行为仿真软件,该模型能够有效量化个体在任务中的工作负荷、任务完成时间及其他相关绩效指标,从而实现对多任务情境下操作员认知负荷等指标的量化评估与预测,为预防操作员认知过载,优化人机交互系统设计提供科学的理论依据与实用的分析工具。
在线报告时间:2026年1月4日(周日)上午10点
腾讯会议报告链接:https://meeting.tencent.com/dm/8ys1UJIBAEQI
腾讯会议号:145-735-219
报告人:浙江理工大学 陈婉婷
2.人的排队网络信息加工模型(QN-MHP)总述
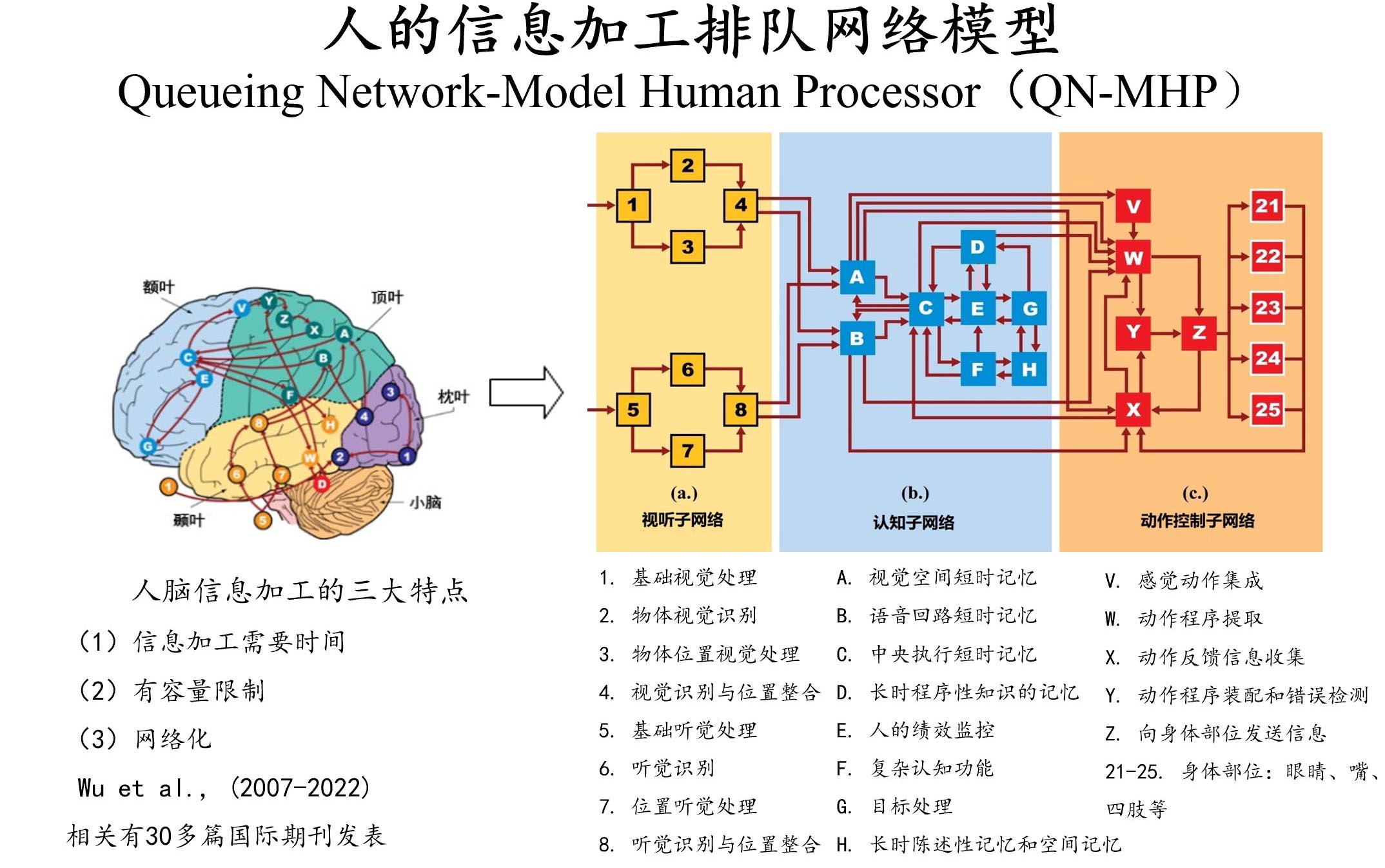
人的排队网络信息加工模型(QN-MHP)整合了应用数学中的排队网络理论和人的信息加工理论模型,能够对人的认
知过程和行为进行预测和仿真,它是自上而下的建模理论,应用于人机系统的设计、评估、优化,提高人机系统的绩效、
安全、满意度和用户体验。
3.QN-MHP部分发表文章全文PDF下载
人的信息加工排队网络模型部分发表文章全文PDF下载:
http://www.renyinbaike.cn/wuchangxu/publications_eng.html
4.QN-MHP建模微信群
欢迎扫描以下二维码加入人的信息加工排队网络模型建模微信群,共同讨论和学习QN-MHP建模:

5.人的建模重要术语
自由参数
自由参数被定义为模型中根据用来验证模型的数据来调整模型以提高模型拟合度的模型参数。
确定系数(R平方)
反映了模型在多大程度上预测了实验数据趋势的变化。
均方根(RMS)
均方根是统计学中的一个术语,用于评估模型预测(x’)与实际数据(x)之间的差异。
6.好的人的绩效模型的标准
机制
好的人的绩效模型应基于人的认知机制。
理论驱动
人的绩效模型应该主要来源于理论预测,而不是从实验数据里面统计或者训练出模型。
实用性
指预测应该直接与人的绩效有关,在现实系统中改善绩效、安全。
鲁棒性
指在异常和特殊情况下的稳定性。
简单性
指模型是基于人的机制做出有用和可靠预测的最简单模型。
7.人的建模的教学视频(部分)
7.1 人的认知和行为建模的学术价值和应用举例
(本短视频版权属于吴昌旭博士和本人因百科网站所有,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意,如需要完整版视频请联系我们(
renyinbaike@163.com)。)
视频地址:
http://www.renyinbaike.cn/video/v10.mp4

7.2 人的认知和行为建模的方法概述
(本短视频版权属于吴昌旭博士和本人因百科网站所有,如需要视频请联系我们,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意(
renyinbaike@163.com)。)

7.3 人的认知和行为建模的5个关键问题
(本短视频版权属于吴昌旭博士和本人因百科网站所有,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意,如需要完整版视频请联系我们(
renyinbaike@163.com)。)
视频地址:
http://www.renyinbaike.cn/video/v3.mp4

7.4 人的认知和行为建模具体案例1:驾驶人建模
(本视频版权属于吴昌旭博士和本人因百科网站所有,如需要视频请联系我们,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意(
renyinbaike@163.com)。)

7.5 人的认知和行为建模具体案例2:视觉追踪和声音技术任务建模
(本短视频版权属于吴昌旭博士和本人因百科网站所有,如需要视频请联系我们,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意(
renyinbaike@163.com)。)

7.6 人的建模及其在舰载人机设备设计中的应用
(本短视频版权属于吴昌旭博士和本人因百科网站所有,如需要视频请联系我们,如果需要商业使用,请先征得我们的同意(
renyinbaike@163.com)。)

8.相关仿真软件
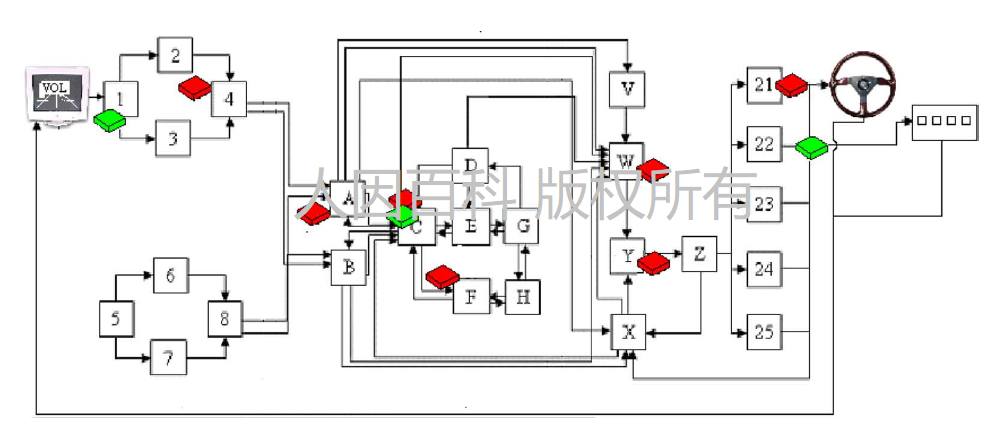
9.人的绩效和认知的数学建模
9.1 人的绩效和认知的数学建模的特点
数学方程式可以严格地预测,量化和分析人类绩效,工作负荷,脑电波和其他人类行为指标。与计算机仿真相比,
1) 我们通过建立人类行为的数学模型和方程式通过变量的关系(包括每个方程的输入和输出之间的关系),能够比较深入地理解和清晰地量化人类行为的机制。读懂数学模型将比阅读上千行计算机代码相更加容易一些,也更容易理解和把握变量之间的关系和人的行为机制。
2) 人类行为的数学模型和方程可以相对大量计算机程序更容易地进行编辑、修改、改进和整合,从而推导出新的数学方程。
3) 人类行为和绩效的数学模型和方程可以相对容易地用不同的编程语言来实现,并且可以嵌入到不同的智能系统中与系统设计一起工作。
4) 数学模型和方程可以得到比仿真结果更精确的解析解。
5) 有一些数学模型和方程量化了整个人类认知系统(见整个网络中的方程式),这是数学建模方法的另一个独特之处。
6) 有一些数学模型和方程式可以通过数学推导直接证明,而无需通过实证数据进行验证(See Equations in Wu, C., Berman, M., & Liu, Y., 2010)
9.2 数学模型和方程式在本总结网页中的使用
这里总结的公式也可以作为索引页和指南工具,供建模人员使用,他们可以:
1) 使用这些数学模型来量化和预测人类绩效中的新现象和新任务
2) 添加和开发新的方程式和数学模型,以量化人类认知和绩效的新成分,并随着人的信息加工排队网络模型(QN-MHP)的框架进一步发展
3) 用于和嵌入到不同的智能系统和工具设计中,对人类绩效和行为进行预测
9.3 学习教程和免费会员资格
1) 如何建立和验证人类绩效模型(概述)(Wu,建模中的五个关键问题)
(视频) [PDF]
2) 如何建立数学模型(例如第9-10页)(Wu & Liu,2008a)(学习视频请联系Dr.Changxu Wu:changxu.wu@gmailcom)
3) 如何在人类绩效建模中整合和建立新的数学模型 (Zhang & Wu, 2017)
4) 若想成为人类绩效数学建模小组的成员(用户或贡献者),获得相关的视频教程(如如何建模),请发送电子邮件至changxu.wu@gmailcom(请列出您的全名和机构/公司名称),我们将向您发送最新的更新、建模工作和教程。
9.4 以人的信息加工排队网络模型为框架的数学方程
整个模型的方程
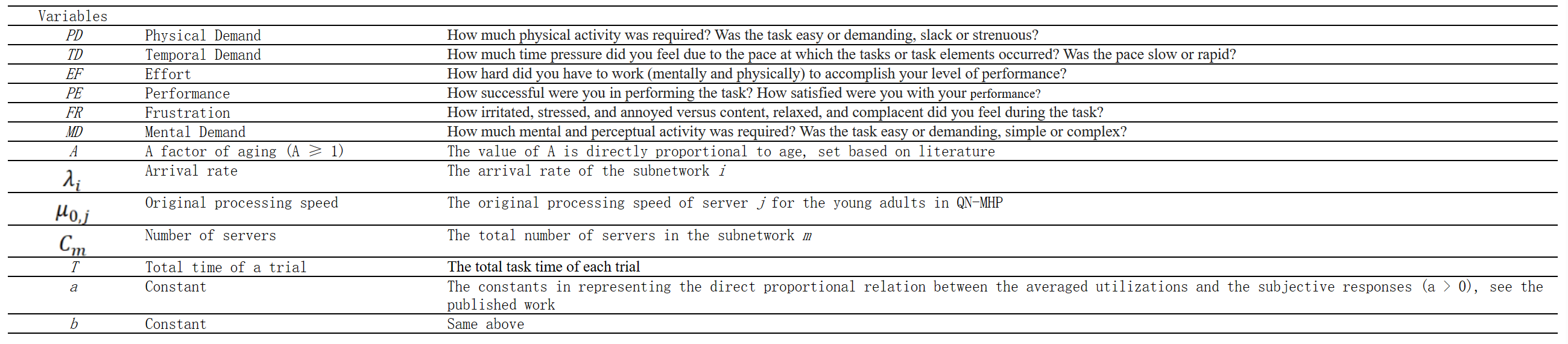
方程组EN-1:NASA-TLX测量的工作负荷建模:方程式(10-12)(Wu & Liu, 2007)
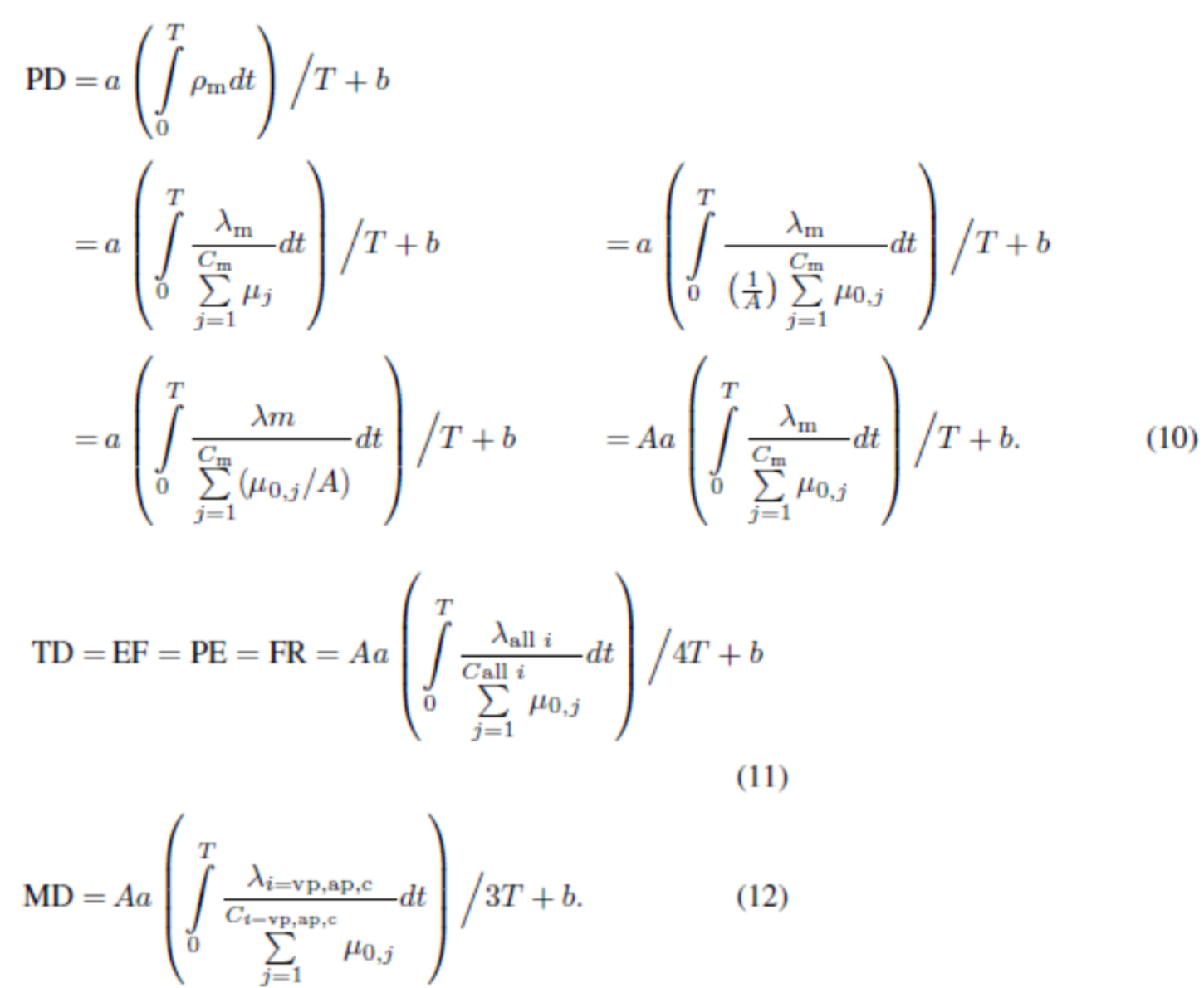
方程组EN-2:以P300波幅和潜伏期衡量的工作负荷建模:方程式(10-11)(Wu, Liu, & Quinn-Walsh, 2008)
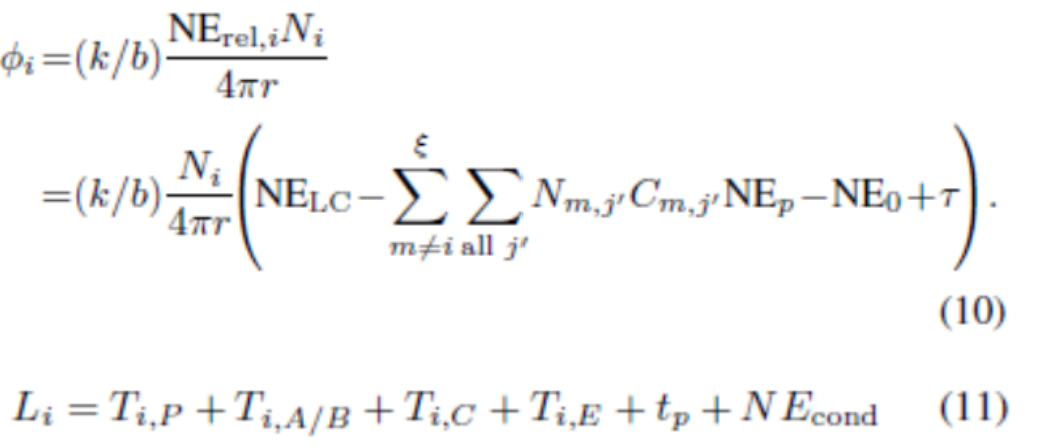

方程组EN-3:在fMRI建模中的Bold信号:方程式(27)(Wu & Liu, 2008a)
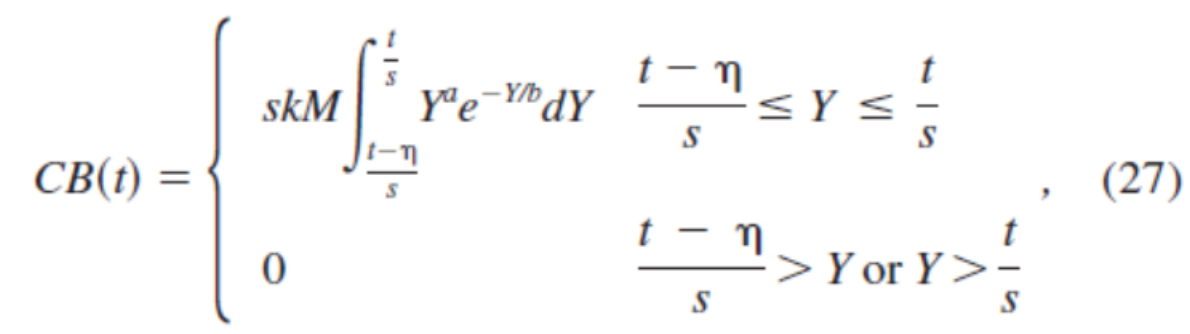
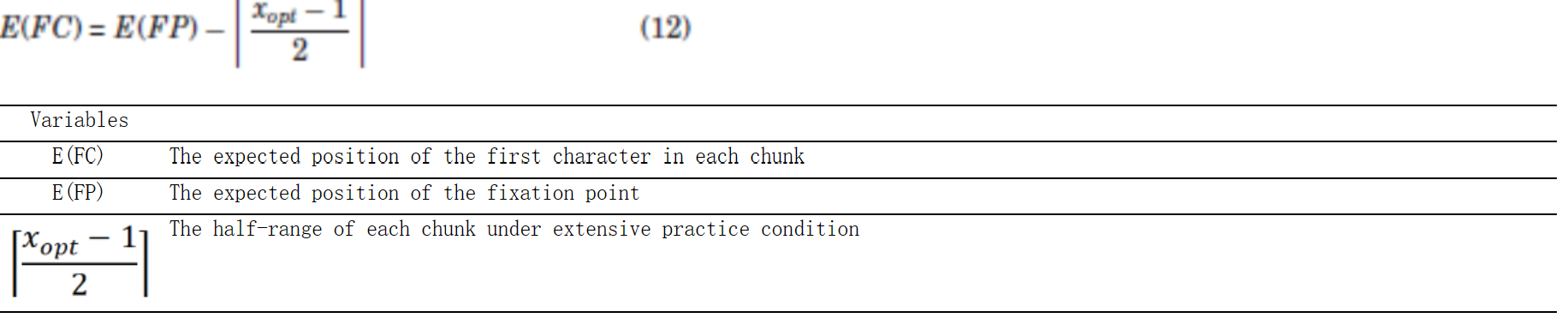
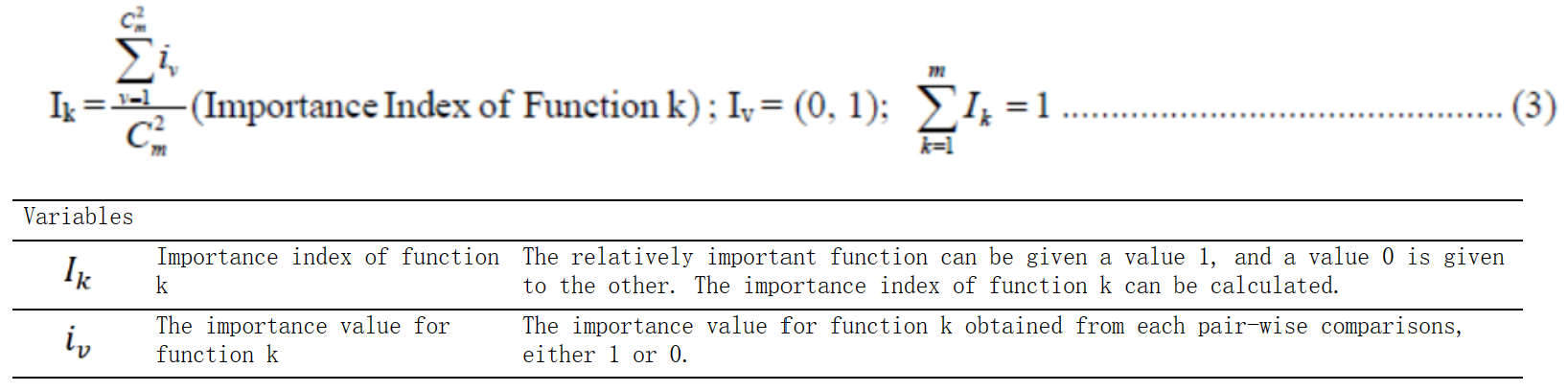
方程组EN-4:基于强化学习算法的实体路线选择和技能获取:方程式(9.7-9.8)(Wu, Berman, & Liu, 2010)

方程组EN-5:学习过程中的信息处理速度及其变异性变化:方程式(6)(Wu & Liu, 2008b)

方程组EN-6:将期望效用建模为时间压力下的工作负荷。方程式(2)(Cao & Liu, 2015)

方程组EN-7:对语音告警的响应时间进行建模。方程式(11,12,13) (Zhang, Wu & Wan, 2016)

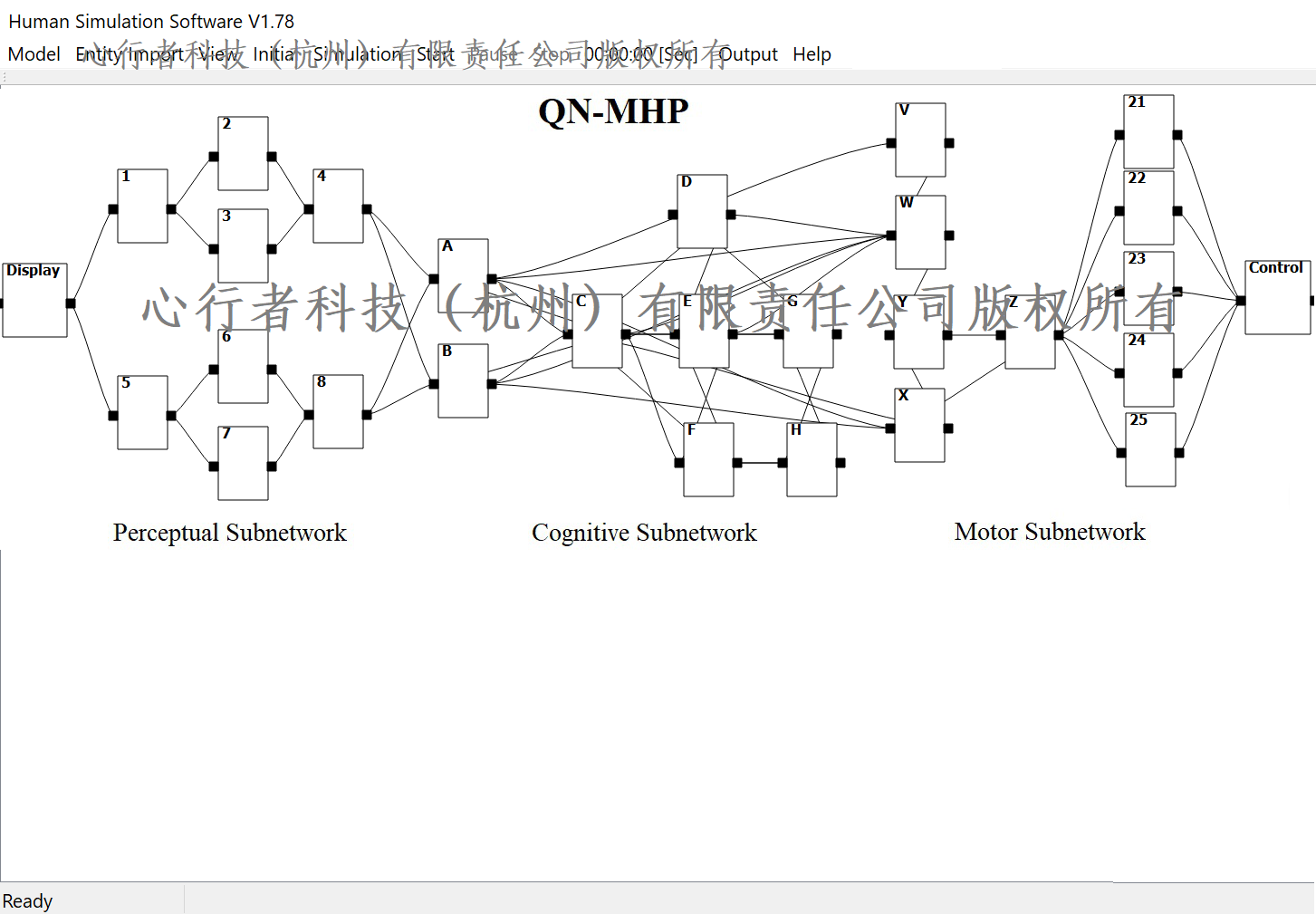
感知子网络
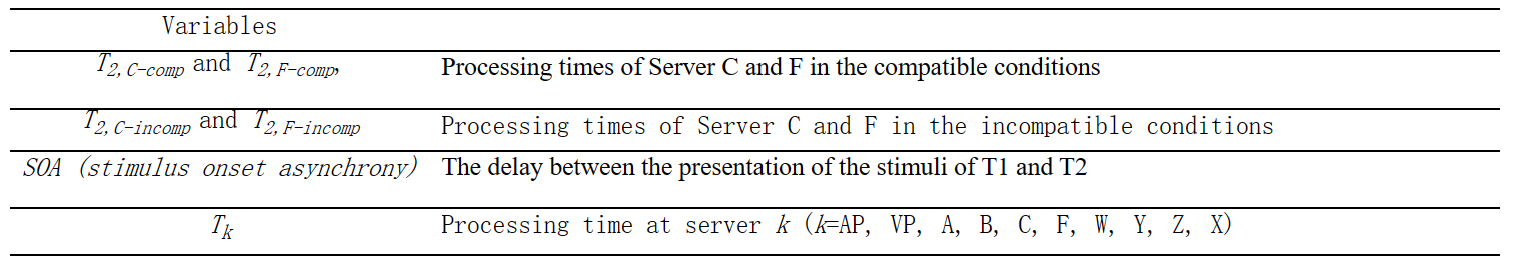
-视觉感知子网络:
服务器1.方程组VP-1:文本信息感知中的眼动建模:方程式(12)(Wu & Liu, 2008b)
服务器1.方程组VP-2:图片信息感知中的眼动建模:方程式(3) (Lim & Liu, 2009)
服务器3.方程组VP-3:视觉光流感知和速度感知:方程(1)(Zhao & Wu, 2013)

服务器4.方程组VP-4:具有检测距离和图像矩阵的视觉检测建模:方程式(12)(Bi, Tsimhoni, & Liu, 2009)

-语音感知子网络:
服务器6.方程组AP-1:模拟响度对语音告警感知的影响:方程式(1,11) (Zhang, Wu, & Wan, 2016)

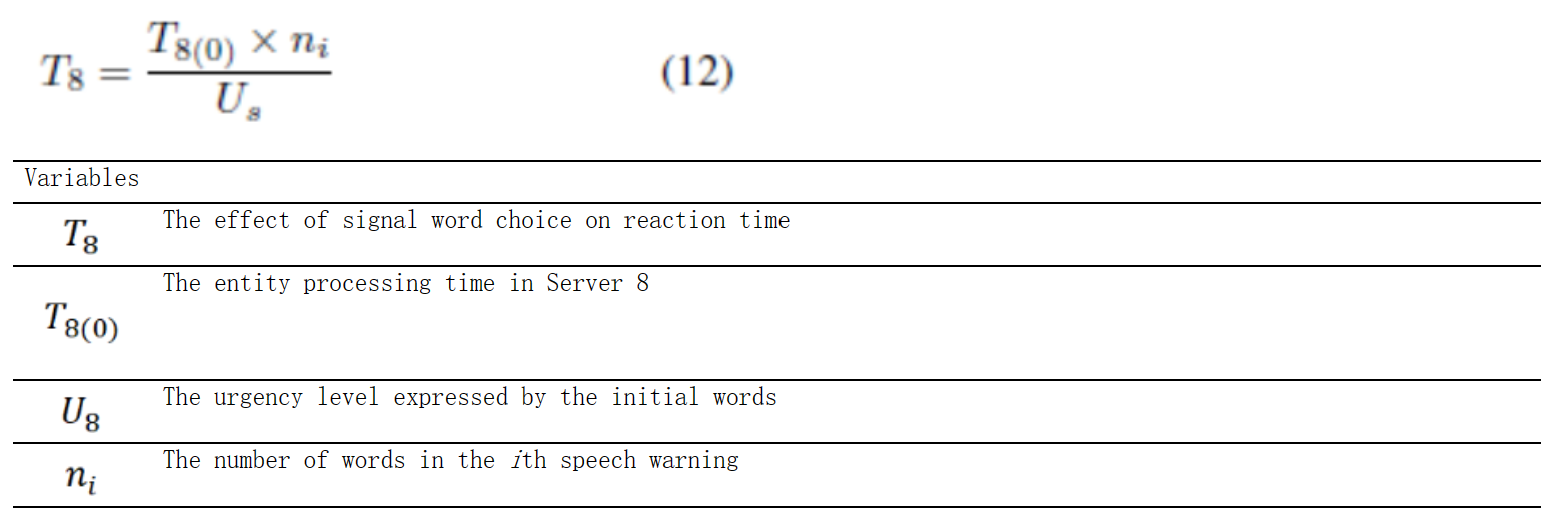
服务器8.方程组AP-2:信号词对语音预警感知的影响建模:方程(12) (Zhang, Wu, & Wan, 2016)
认知子网络
-服务器B:
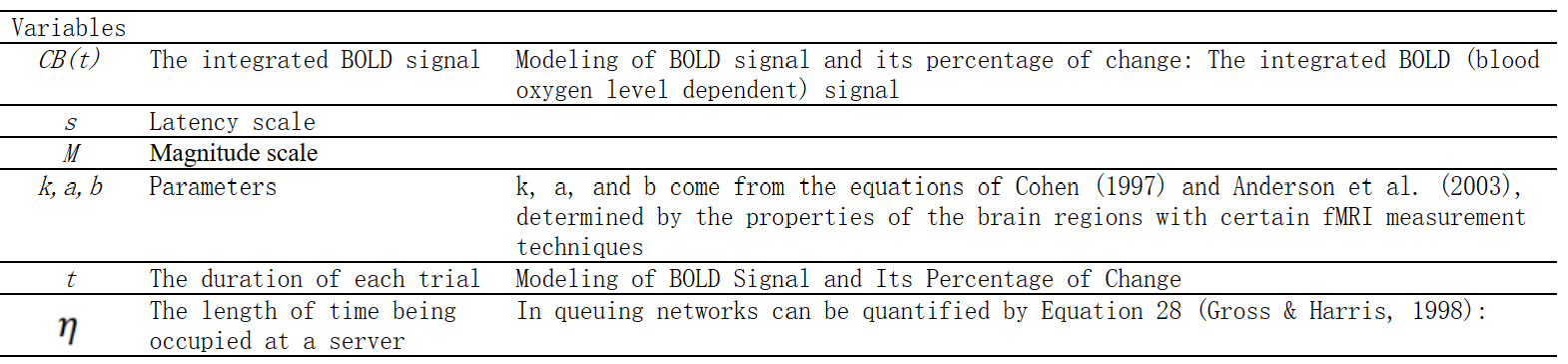
方程组C-1:文本信息的最优分块建模:方程式(22) (Wu & Liu, 2008b)

方程组C-2:语音信息记忆衰减的建模:方程(7) ( Zhang, Wu, & Wan, 2016)

方程组C-3:对语音告警的强化学习中的路径选择概率进行建模:方程式(4-5) ( Zhang, Wu, & Wan, 2016)

-服务器C:
方程组C-4:抑制不相容反应建模:方程式(4-6) (Wu & Liu, 2008a)
方程组C-5:双重任务干扰建模:方程式(8-9) (Lin & Wu, 2012)

-服务器E:
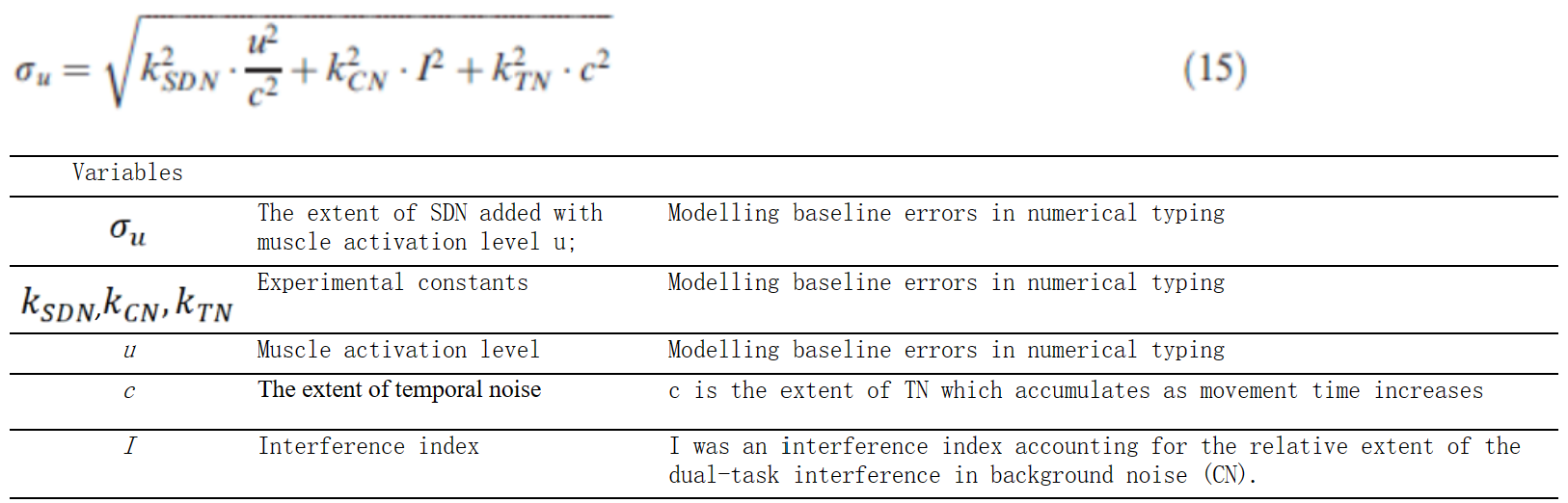
方程组C-6:动作控制中的背景噪声:方程式(15) (Lin & Wu, 2012)
-服务器F:
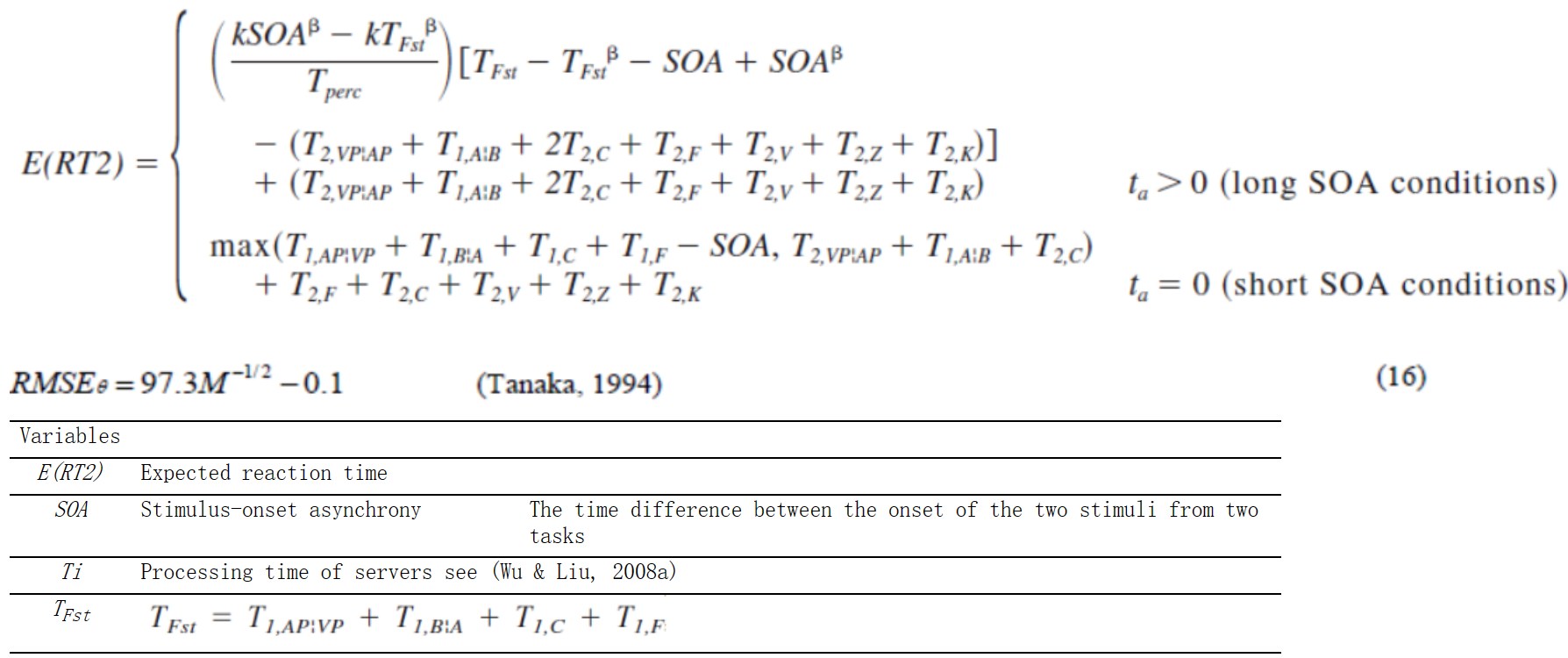
方程组C-7:多任务中的选择反应建模:方程式(B16) (Wu & Liu, 2008a)
方程组C-8:建模响应复杂度的影响(同时使用一个手指或多个手指):公式(1-13)(Lin & Wu, 2012)

方程组C-9:具有值矩阵的复杂决策:公式(5)(Zhao & Wu, 2013)
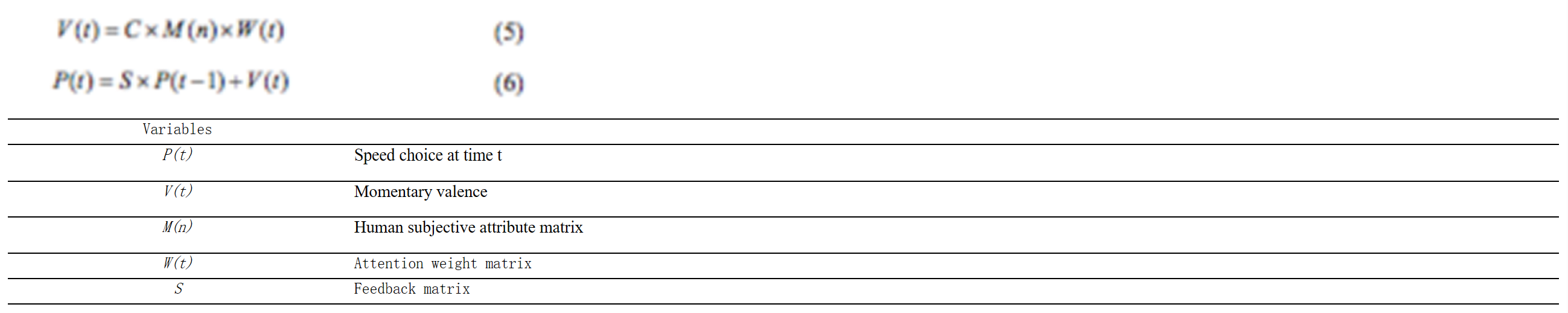
方程组C-10:感知风险建模:方程式(5) (Zhuang & Wu, 2013)
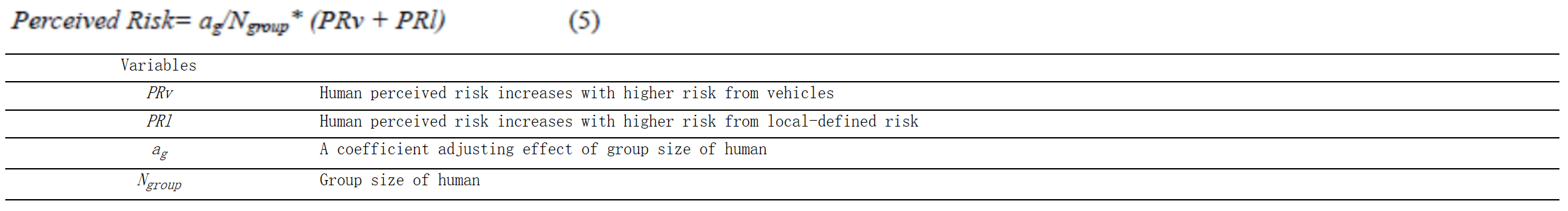
方程组C-11:横向控制决策:方程式(1,2) (Bi, Gan, Shang, & Liu, 2012)
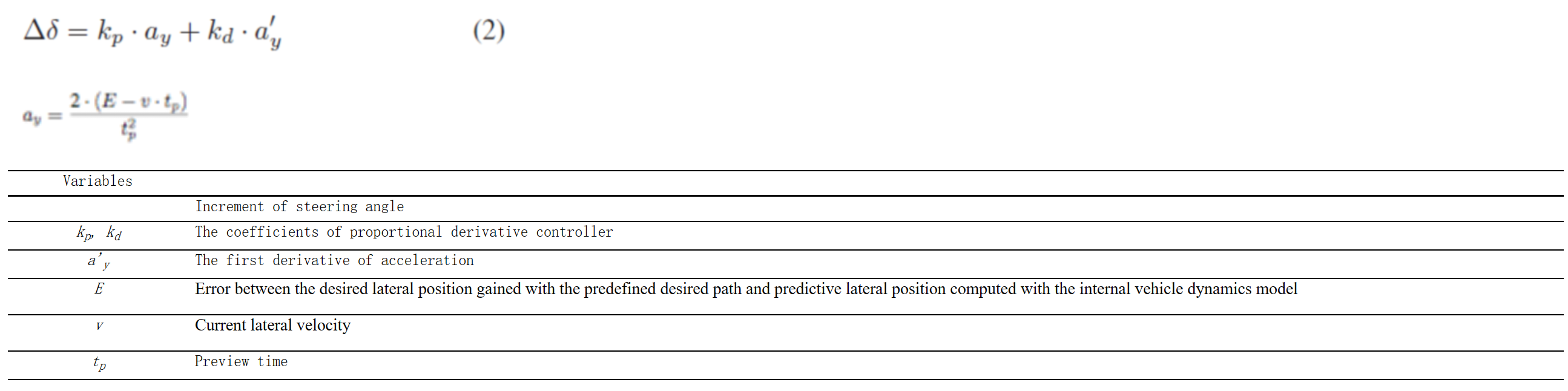
方程组C-12:对风险评估的准确性建模:方程式(8,16,21)( Zhang, Wu, & Wan, 2016)

-服务器G:
方程组C-13:紧迫性和动机建模:方程式(12) (Lin & Wu, 2012)
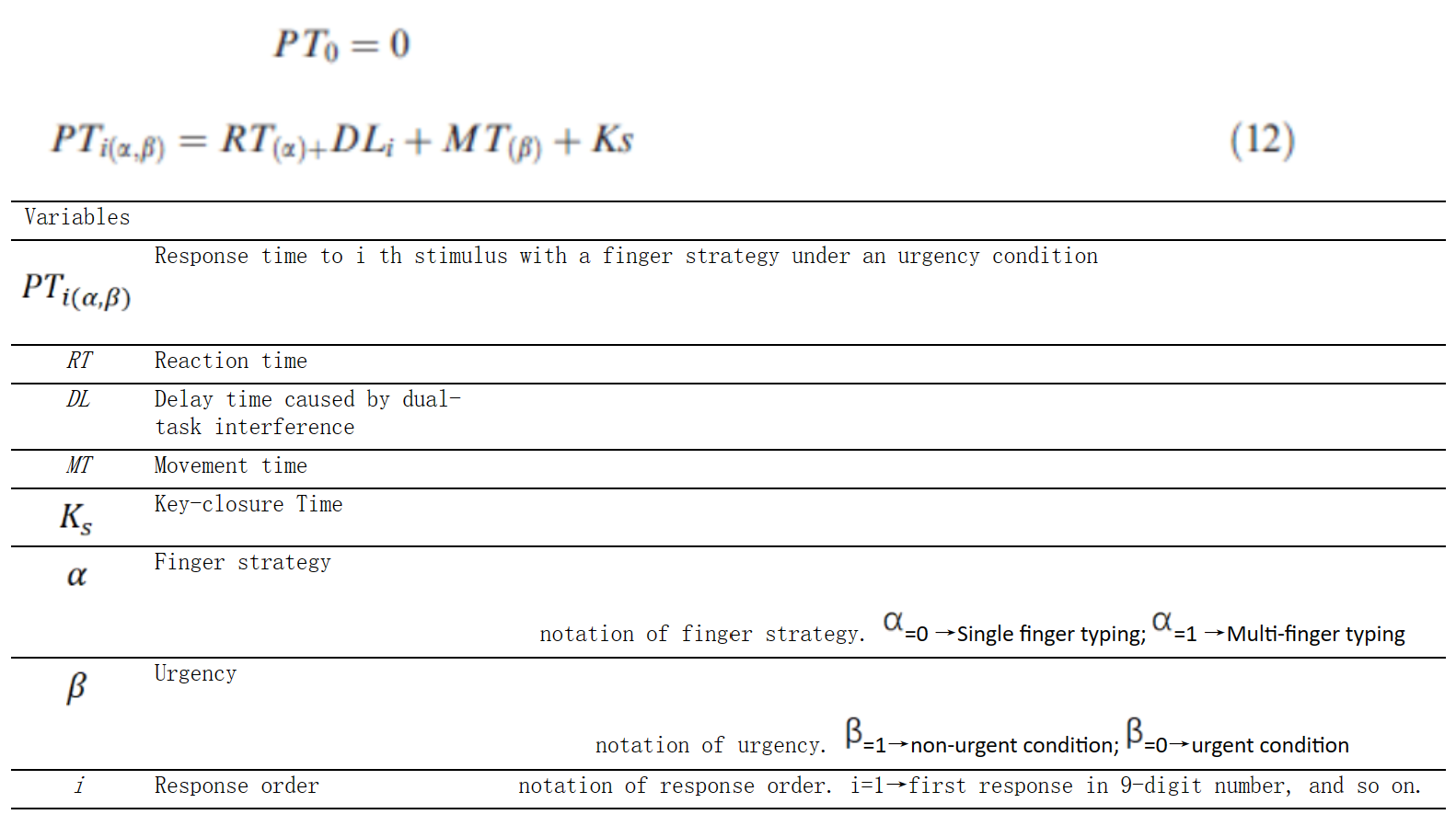
动作控制子网络
-服务器W:
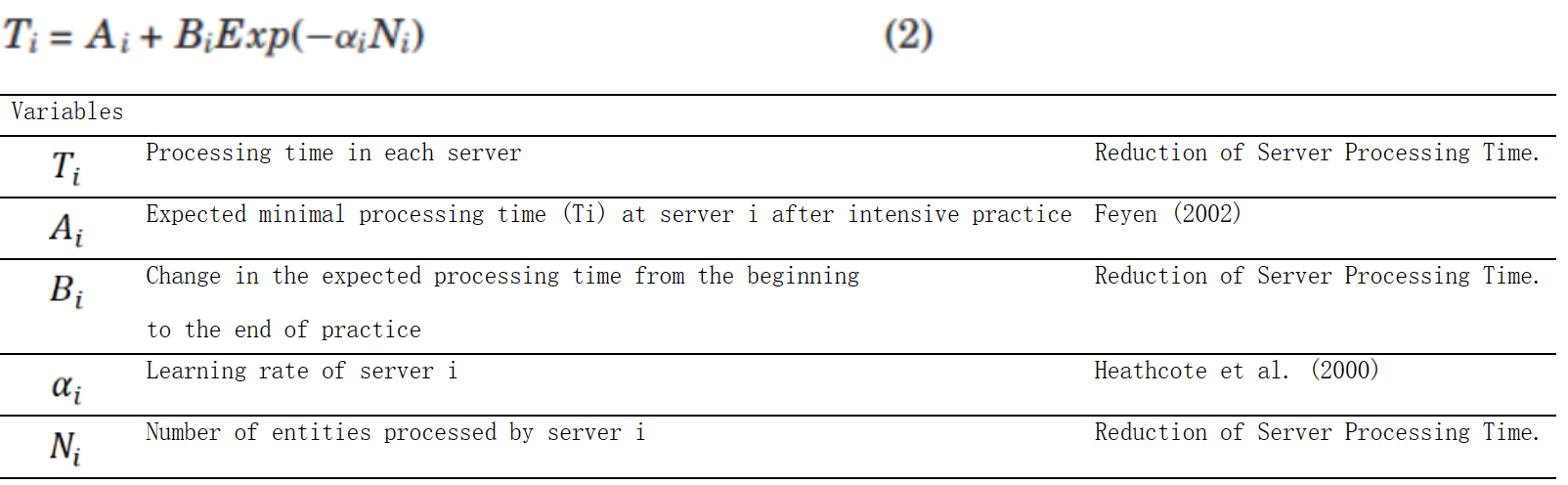
-服务器X:
方程组M-2:闭环动作控制中的误差校正模型:方程式(24-32)(Lin & Wu, 2012)
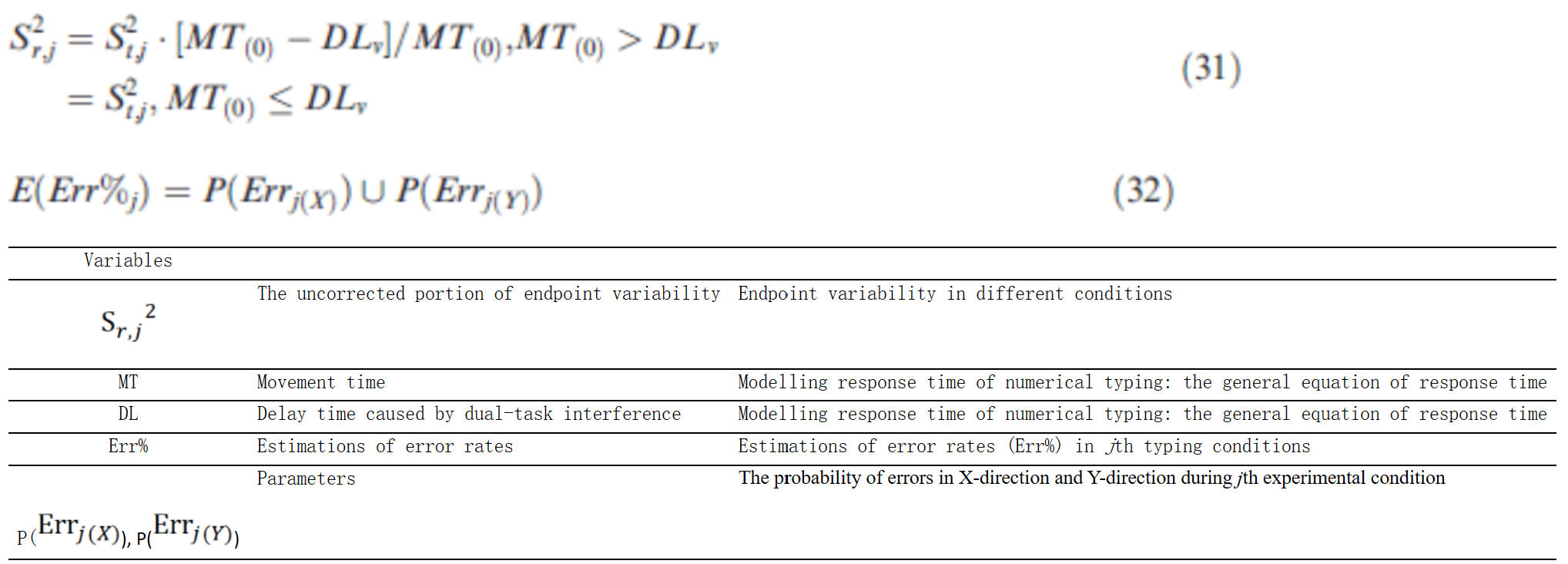
-手服务器(服务器23,24):
方程组M-3:QWERTY键盘输入中手和手指移动的时间和错误:方程式(19) (Wu & Liu, 2008b)
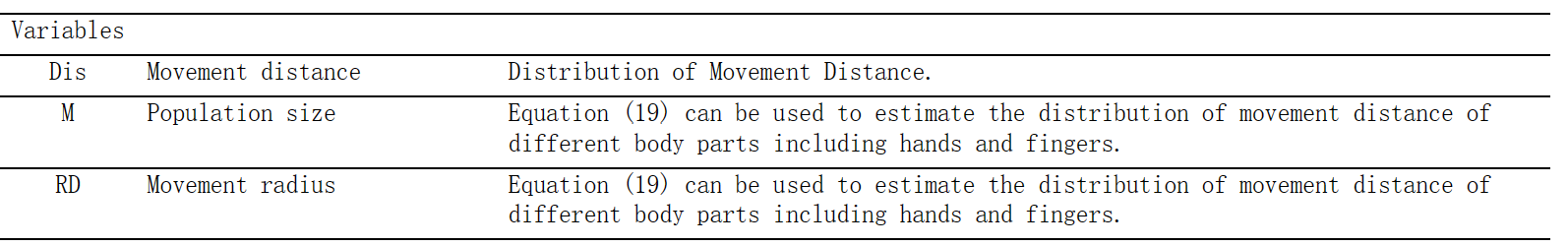
方程组M-4:双手(两只手)配合:方程(31-34)(Wu & Liu, 2008b)
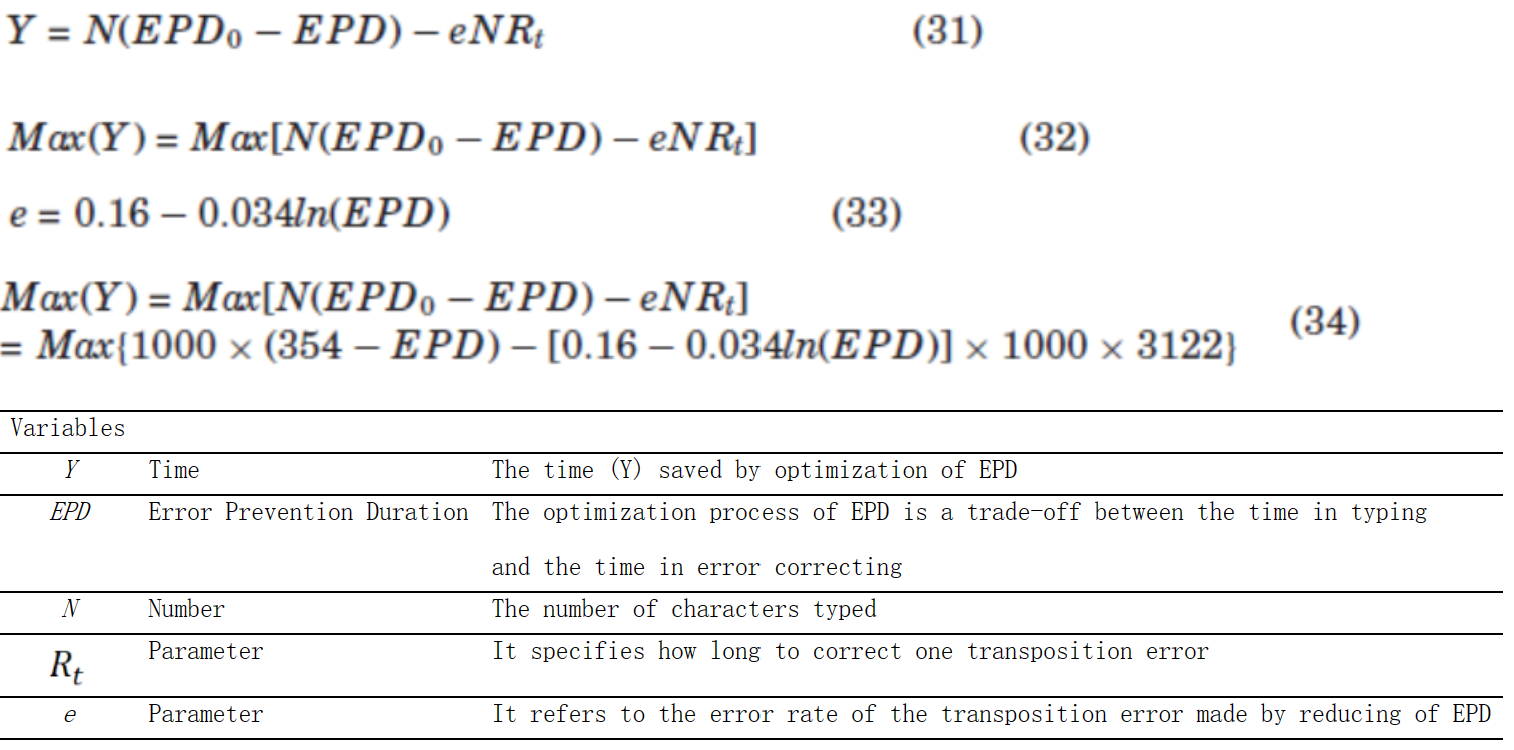
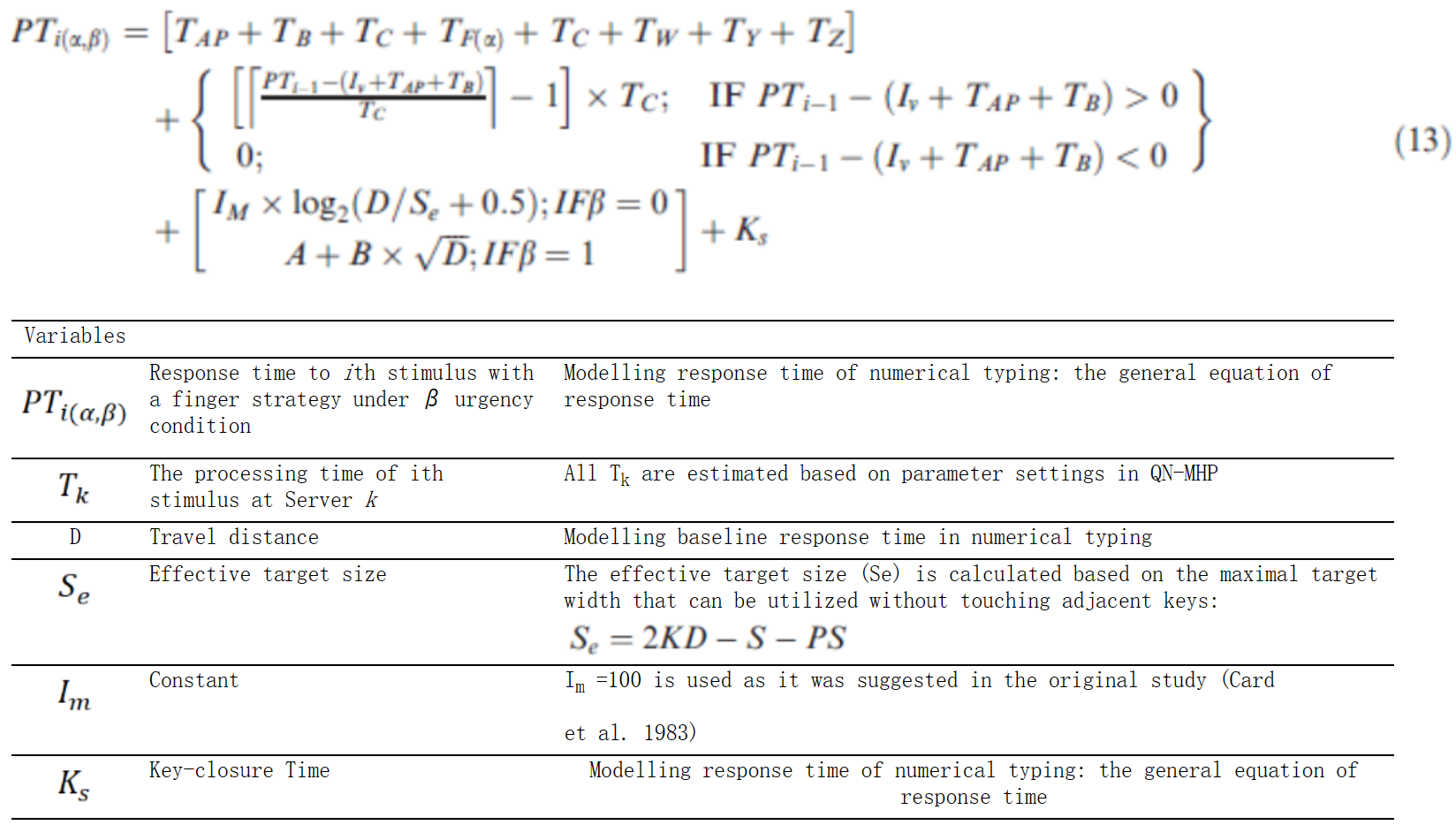
方程组M-5:数字打字中的手和手指移动时间和错误:方程式(13)(16) (Lin & Wu, 2012)
-脚服务器(服务器25)
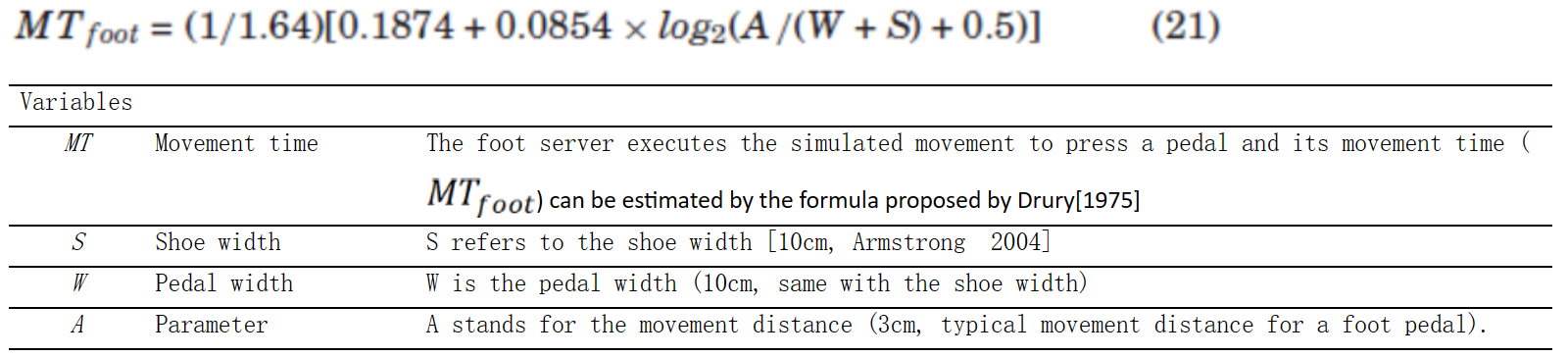
方程组M-6:脚踩踏板时的运动时间:方程式(21) (Wu & Liu, 2008b)
方程组M-7:不考虑人的个性作为个体差异因素的脚部运动的角速度:方程式(3) (Zhao, Wu, & Qiao, 2013)
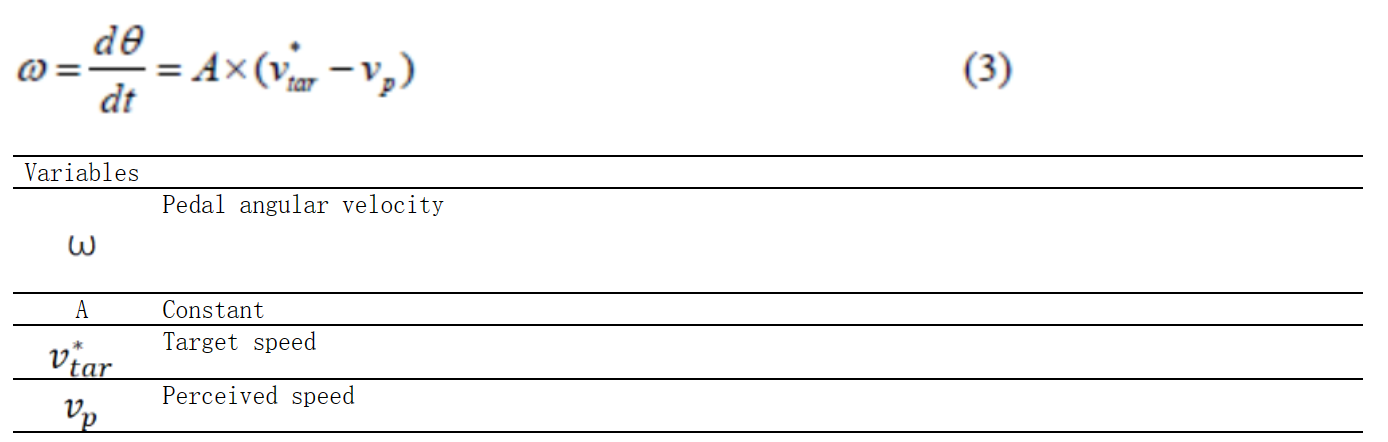

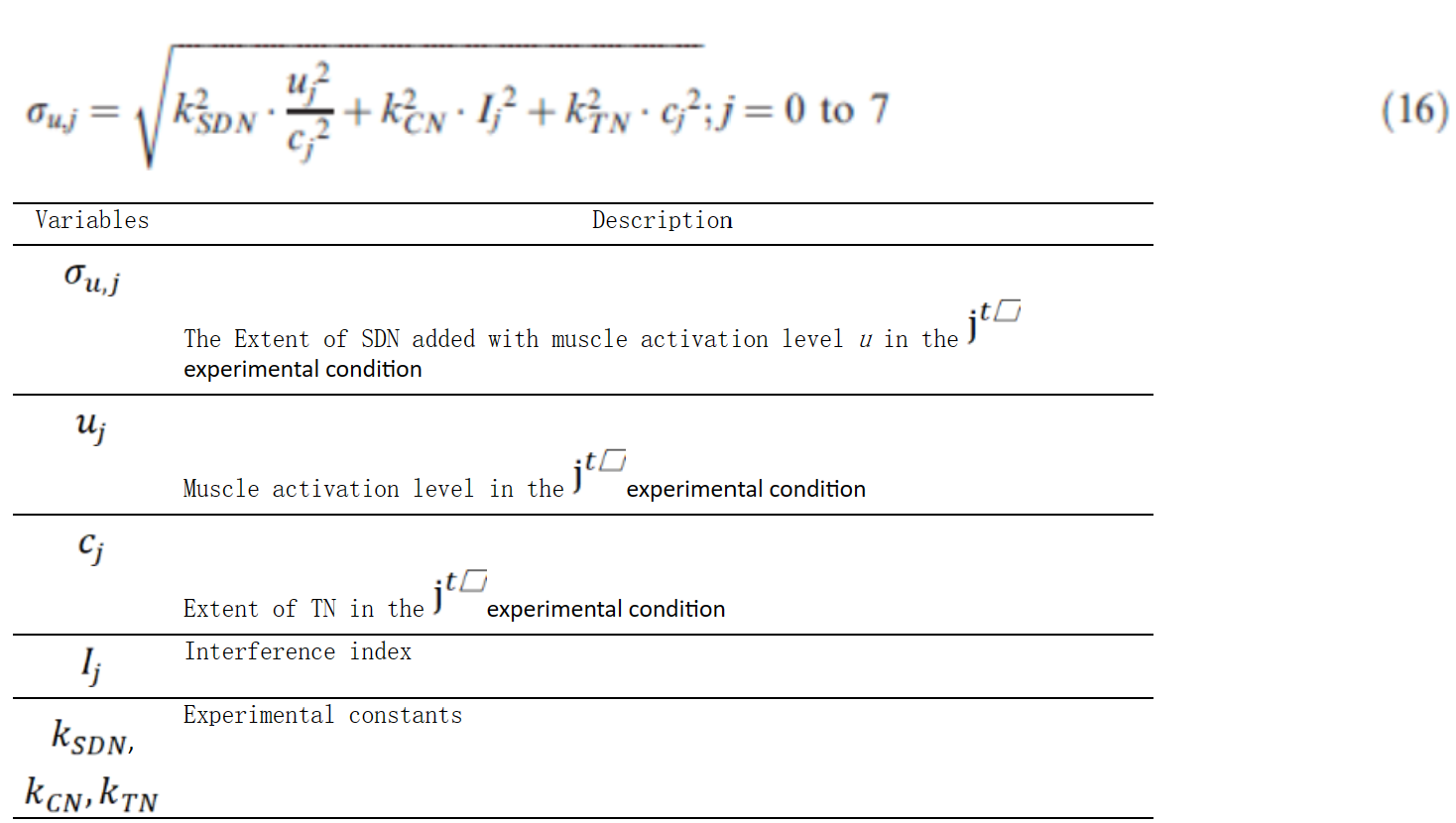
方程组M-8:考虑人的个性作为个体差异因素的脚部运动的角速度 (Zhao & Wu, 2013)(Zhao & Wu, 2013)

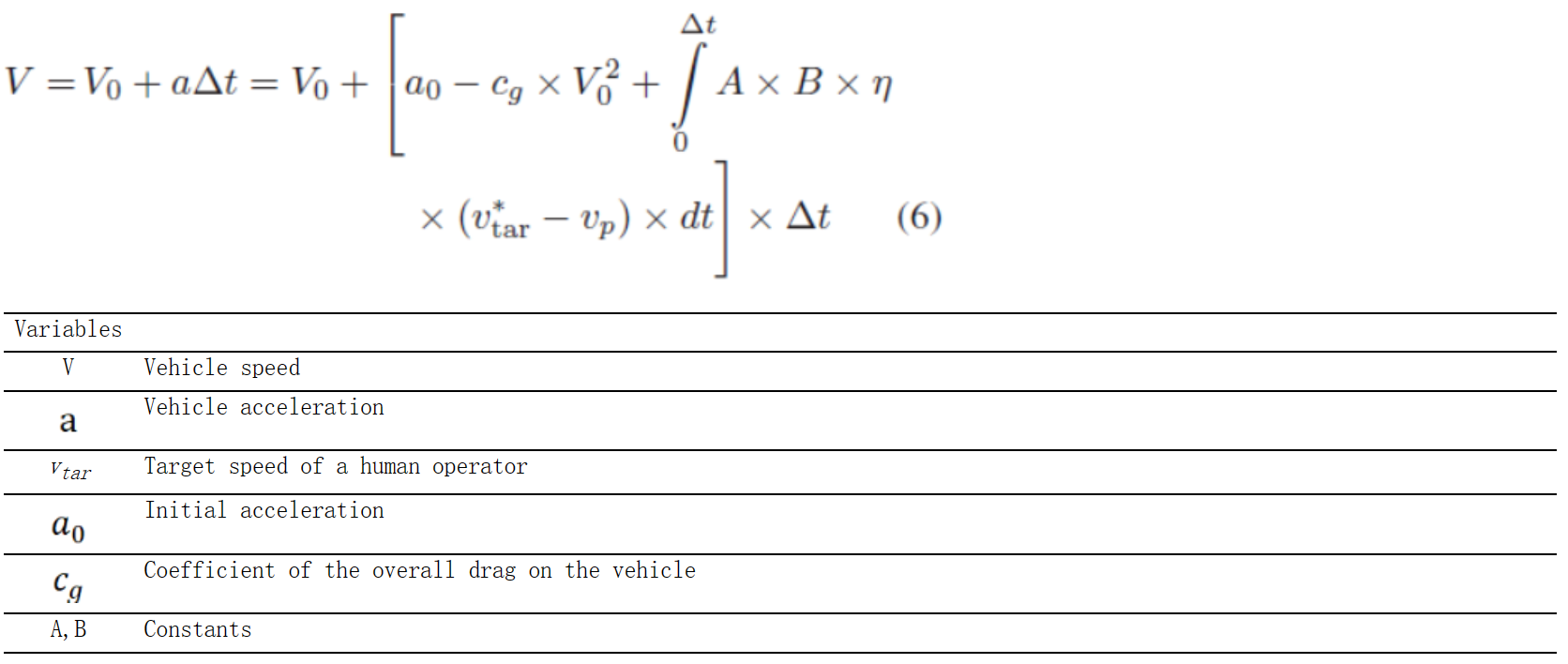
方程组M-9:人的目标速度对车辆运动速度的影响:方程(6)(Zhao & Wu, 2013)
9.5 使用QN-MHP对人的绩效进行数学建模的主要贡献者(欢迎加入我们!Email:changxuwu@gmail.com)
我们特别感谢密歇根大学的Dr. Yili Liu,他用排队网络理论统一了现有的反应时间模型,为人的绩效的排队网络建模奠定了理论基础。
Dr. Changxu Wu (Group Coordinator) at University of Arizona, USA
Dr. Robert Feyen, University of Minnesota, USA
Dr. Omer Tsimhoni, General Motors, USA
Dr. Ji Hyoun Lim, Apple, USA; Hongik University, Korea
Dr. Luzheng Bi at Beijing Institute of Technology, China
Dr. Shi Cao at University of Waterloo, Canada
Dr. Guozhen Zhao at Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Dr. Cheng-Jhe (Robert) Lin, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology
Dr. Jingyan Wan, General Motors, USA
Dr. Yiqi Zhang at Pen State University, USA
9.6 发表QN-MHP模型文章的国内外科研机构
美国密歇根大学
美国杜克大学
美国宾夕法尼亚州立大学
美国纽约州立大学
美国亚利桑那大学
美国密歇根理工大学
韩国首尔大学
清华大学
中国科学院
台湾清华大学
北京理工大学
四川大学
9.7 发表QN-MHP模型文章的国内外科研机构
Bi, L. Z., Gan, G. D., Shang, J. X., & Liu, Y. L. (2012). Queuing Network Modeling of Driver Lateral Control With or Without a Cognitive Distraction Task [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 13(4), 1810-1820. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tits.2012.2204255
Bi, L. Z., Tsimhoni, O., & Liu, Y. L. (2009). Using Image-Based Metrics to Model Pedestrian Detection Performance With Night-Vision Systems [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 10(1), 155-164. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tits.2008.2011719
Bi, L. Z., Wang, M. T., Wang, C. E., & Liu, Y. L. (2015). Development of a Driver Lateral Control Model by Integrating Neuromuscular Dynamics Into the Queuing Network-Based Driver Model [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 16(5), 2479-2486. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tits.2015.2409115
Cao, S., & Liu, Y. (2015). Modelling workload in cognitive and concurrent tasks with time stress using an integrated cognitive architecture. International Journal of Human Factors Modelling and Simulation, 5(2), 113-135. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijhfms.2015.075360
Chikodili, H. U., Mathew, C. O., & Caroline, N. A. (2017). Performance evaluation of law enforcement agency on crime information management using queuing network model. International Journal of Physical Sciences, 12(4), 38-51. https://doi.org/10.5897/ijps2016.4581
Feng, F., Liu, Y., Chen, Y., Filev, D., & To, C. (2014). Computer-aided usability evaluation of in-vehicle infotainment systems. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting,
Feng, F., Liu, Y. L., & Chen, Y. F. (2017). A computer-aided usability testing tool for in-vehicle infotainment systems [Article]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 109, 313-324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2017.05.019
Fu, X. L., Cai, L. H., Liu, Y., Jia, J., Chen, W. F., Yi, Z., Zhao, G. Z., Liu, Y. J., & Wu, C. X. (2014). A computational cognition model of perception, memory, and judgment [Article]. Science China-Information Sciences, 57(3), 15, Article 032114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-013-4911-9
Fuller, H. J., Reed, M. P., & Liu, Y. (2010). Integrating physical and cognitive human models to represent driving behavior. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting,
Fuller, H. J. A., Reed, M. P., & Liu, Y. L. (2012). Integration of Physical and Cognitive Human Models to Simulate Driving With a Secondary In-Vehicle Task [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 13(2), 967-972. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tits.2012.2182764
Gil, G. H., & Kaber, D. B. (2012). An Accessible Cognitive Modeling Tool for Evaluation of Pilot-Automation Interaction [Article]. International Journal of Aviation Psychology, 22(4), 319-342. https://doi.org/10.1080/10508414.2012.718236
Jeong, H., & Liu, Y. (2016). Computational Modeling of Finger Swipe Gestures on Touchscreen: Application of Fitts’ Law in 3D Space. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting,
Jeong, H., & Liu, Y. L. (2019). Computational Modeling of Touchscreen Drag Gestures Using a Cognitive Architecture and Motion Tracking [Article]. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 35(6), 510-520. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2018.1466858
Ko, S., Kutchek, K., Zhang, Y., & Jeon, M. (2021). Effects of Non-Speech Auditory Cues on Control Transition Behaviors in Semi-Automated Vehicles: Empirical Study, Modeling, and Validation [Article]. International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction, 38(2), 185-200. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2021.1937876
Li, H., Bi, L., & Shi, H. (2020). Modeling of Human Operator Behavior for Brain-Actuated Mobile Robots Steering [Article]. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng, 28(9), 2063-2072. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2020.3009376
Lim, J. H., & Liu, Y. (2004). A queuing network model for visual search and menu selection. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting,
Lim, J. H., & Liu, Y. L. (2009). Modeling the Influences of Cyclic Top-Down and Bottom-Up Processes for Reinforcement Learning in Eye Movements [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics Part a-Systems and Humans, 39(4), 706-714. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tsmca.2009.2018635
Lim, J. H., Liu, Y. L., & Tsimhoni, O. (2010). Investigation of Driver Performance With Night-Vision and Pedestrian-Detection Systems-Part 2: Queuing Network Human Performance Modeling [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 11(4), 765-772. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tits.2010.2049844
Lin, B. T. W., & Hwang, S. L. (2012). Effect prediction of time-gaps for adaptive cruise control (ACC) and in-vehicle tasks on bus driver performance [Article]. Safety Science, 50(1), 68-75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2011.07.003
Lin, C.-J., Wu, C., & Chaovalitwongsec, W. A. (2014). Integrating behavior modeling with data mining to improve human error prediction in numerical data entry. Proceedings of the human factors and ergonomics society annual meeting,
Lin, C. J., & Wu, C. (2012). Mathematically modelling the effects of pacing, finger strategies and urgency on numerical typing performance with queuing network model human processor [Article]. Ergonomics, 55(10), 1180-1204. https://doi.org/10.1080/00140139.2012.697583
Lin, C. J., Wu, C. X., & Chaovalitwongse, W. A. (2015). Integrating Human Behavior Modeling and Data Mining Techniques to Predict Human Errors in Numerical Typing [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Human-Machine Systems, 45(1), 39-50. https://doi.org/10.1109/Thms.2014.2357178
Liu, Y., Feyen, R., & Tsimhoni, O. (2006). Queueing Network-Model Human Processor (QN-MHP). Acm Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction, 13(1), 37-70. https://doi.org/10.1145/1143518.1143520
Liu, Y., & Wu, C. (2006). Modeling Percentage Change of fMRI BOLD Signal and Reaction Time of a Dual Task with a Queuing Network Modeling Approach. Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society,
Liu, Y., Wu, C., & Berman, M. G. (2012). Computational neuroergonomics [Article]. Neuroimage, 59(1), 109-116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.05.027
Liu, Y. L. (2009). QN-ACES: Integrating Queueing Network and ACT-R, CAPS, EPIC, and Soar Architectures for Multitask Cognitive Modeling [Article]. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 25(6), 554-581, Article Pii 913657582. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447310902973182
Rhie, Y. L., Lim, J. H., & Yun, M. H. (2019). Queueing Network Based Driver Model for Varying Levels of Information Processing [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Human-Machine Systems, 49(6), 508-517. https://doi.org/10.1109/Thms.2018.2874183
Tsimhoni, O., & Liu, Y. (2003). Modeling steering using the queueing network—model human processor (QN-MHP). Proceedings of the human factors and ergonomics society annual meeting,
Tsimhoni, O., & Reed, M. P. (2007). The virtual driver: Integrating task planning and cognitive simulation with human movement models. SAE Transactions, 1525-1531. https://doi.org/10.4271/2007-01-1766
Wu, C. (2018). The Five Key Questions of Human Performance Modeling [Article]. Int J Ind Ergon, 63, 3-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ergon.2016.05.007
Wu, C., & Liu, Y. (2004). Modeling human transcription typing with queuing network-model human processor (QN-MHP). Proceedings of the human factors and ergonomics society annual meeting,
Wu, C., & Liu, Y. (2006). Queuing network modeling of age differences in driver mental workload and performance. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting,
Wu, C., & Liu, Y. (2008a). Queuing network modeling of the psychological refractory period (PRP). Psychol Rev, 115(4), 913-954. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0013123
Wu, C., & Liu, Y. (2008b). Queuing network modeling of transcription typing [Review]. Acm Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction, 15(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.1145/1352782.1352788
Wu, C. X., Liu, Y. J., & Lin, B. (2012). A Queueing Model Based Intelligent Human-Machine Task Allocator [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 13(3), 1125-1137. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tits.2012.2187351
Wu, C. X., & Liu, Y. L. (2007a). Queuing network modeling of driver workload and performance [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 8(3), 528-537. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tits.2007.903443
Wu, C. X., & Liu, Y. L. (2007b). Usability Makeover of a Cognitive Modeling Tool [Editorial Material]. Ergonomics in Design, 15(2), 8-14. https://doi.org/Doi 10.1177/106480460701500201
Wu, C. X., & Liu, Y. L. (2009). Development and evaluation of an ergonomic software package for predicting multiple-task human performance and mental workload in human-machine interface design and evaluation [Article]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 56(1), 323-333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2008.06.013
Wu, C. X., Liu, Y. L., & Quinn-Walsh, C. M. (2008). Queuing network modeling of a real-time psychophysiological index of mental workload - P300 in event-related potential (ERP) [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics Part a-Systems and Humans, 38(5), 1068-1084. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tsmca.2008.2001070
Wu, C. X., Tsimhoni, O., & Liu, Y. L. (2008). Development of an adaptive workload management system using the queueing network-model human processor (QN-MHP) [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 9(3), 463-475. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tits.2008.928172
Zhang, Y., & Wu, C. (2014). Modeling the effect of loudness and semantics of speech warnings on human performances. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting,
Zhang, Y., & Wu, C. (2017). Learn to integrate mathematical models in human performance modeling. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting,
Zhang, Y. Q., Wu, C. X., Qiao, C. M., Sadek, A., & Hulme, K. F. (2022). A Cognitive Computational Model of Driver Warning Response Performance in Connected Vehicle Systems [Article; Early Access]. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 16. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tits.2021.3134058
Zhang, Y. Q., Wu, C. X., & Wan, J. Y. (2016). Mathematical Modeling of the Effects of Speech Warning Characteristics on Human Performance and Its Application in Transportation Cyberphysical Systems [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 17(11), 3062-3074. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tits.2016.2539975
Zhang, Y. Q., Wu, C. X., & Wan, J. Y. (2017). A human-in-the-loop wireless warning message notification model and its application in connected vehicle systems [Article]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 21(2), 148-166. https://doi.org/10.1080/15472450.2016.1254045
Zhao, G., Wu, C., & Ou, B. (2011). Mathematical modeling of average driver speed control with the integration of queuing network-model human processor and rule-based decision field theory. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting,
Zhao, G. Z., & Wu, C. X. (2013). Mathematical Modeling of Driver Speed Control With Individual Differences [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Systems Man Cybernetics-Systems, 43(5), 1091-1104. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tsmc.2013.2256854
Zhao, G. Z., Wu, C. X., & Qiao, C. M. (2013). A Mathematical Model for the Prediction of Speeding with its Validation [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 14(2), 828-836. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tits.2013.2257757
Zhuang, X. L., & Wu, C. X. (2013). Modeling Pedestrian Crossing Paths at Unmarked Roadways [Article]. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 14(3), 1438-1448. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tits.2013.2267734
若要成为人类绩效建模中数学建模小组的成员(用户或贡献者),请发送电子邮件至changxu.wu@gmailcom(请列出您的全名和机构/公司名称),我们将向您发送最新更新,新的建模工作,和新教程。所有这些都是免费的。
10.参考书目
以上部分内容引用自《人因工程:原理、方法和设计》(清华大学出版社,预计2023年正式出版)